In every modern organization, the most valuable resource is not data itself — it’s the ability to find, understand, and use it efficiently.
Yet, most companies are sitting on thousands of documents, spreadsheets, ERP records, and emails that remain disconnected and underused.
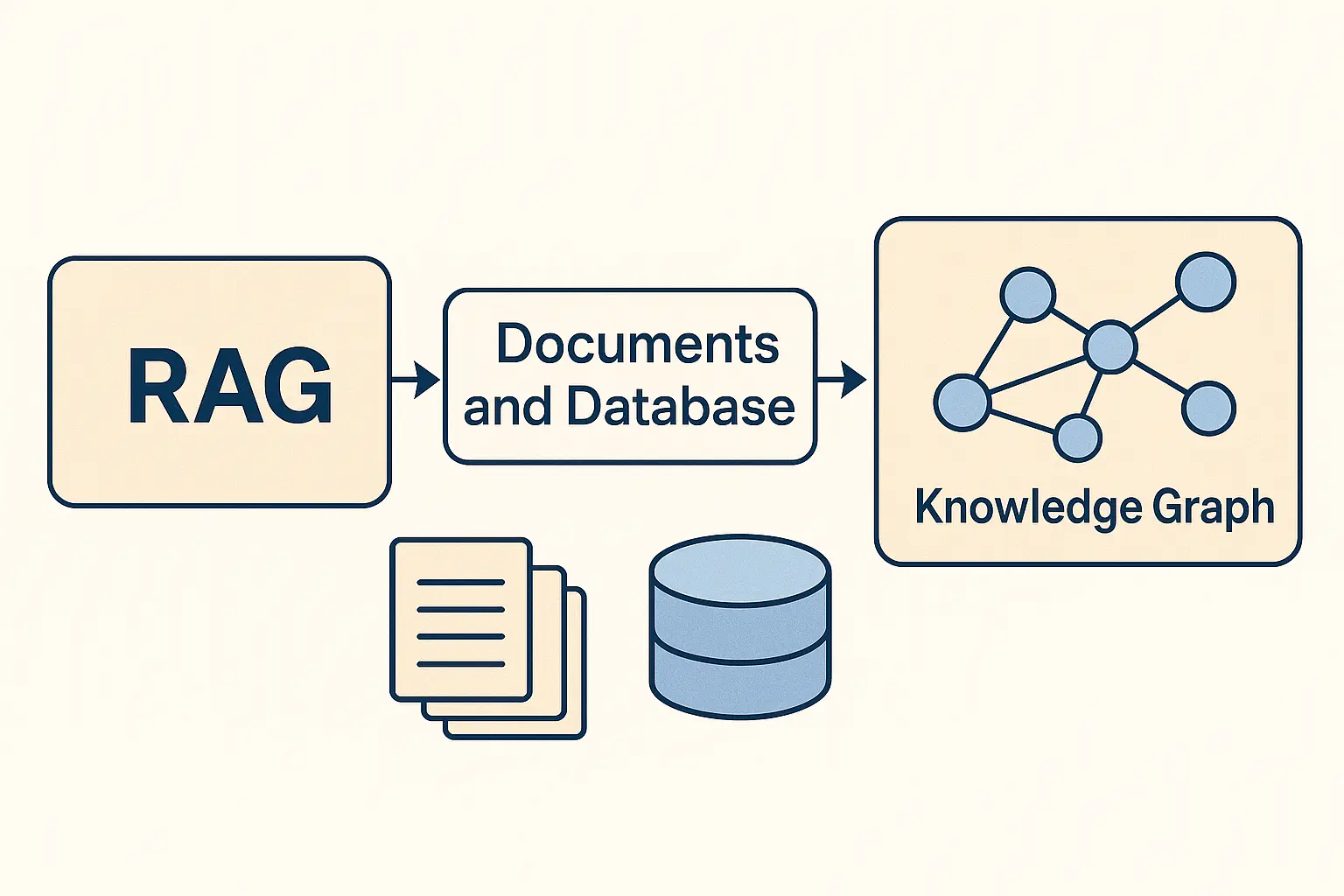
This is where RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and Knowledge Graphs come into play.
Together, they combine your existing business data with the power of large language models (LLMs) — transforming static information into an intelligent, contextual, and conversational layer for decision-making.
What is RAG?
RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, is an architecture that enhances language models by connecting them to external data sources such as your business documents, databases, or ERP systems.
Instead of relying only on the model’s built-in training data, RAG retrieves the most relevant information from your own sources at the time of the question and uses that content to generate precise, contextual, and verifiable answers.
It’s like giving your company an AI assistant that truly knows your business — because it’s powered by your own data.
Why It Matters for Your Business
Every company faces the same challenge: the larger and more complex your operations become, the harder it is to access reliable information quickly.
Executives, managers, and analysts often waste hours searching across systems — Oracle E-Business Suite, Oracle Cloud, SharePoint, CRMs, local folders — to find a single answer about a contract, supplier, tax configuration, or transaction.
With a properly designed RAG layer, that friction disappears.
You can simply ask:
“Show me all open purchase orders above 100,000 BRL linked to the Hemobrás 001 organization.”
Or:
“Summarize the tax rules that will change with the 2026 Brazilian IBS/CBS reform.”
And get the correct, contextual answer — complete with citations from your documents or databases.
How RAG Works
At a high level, a RAG system has three main components:
- Data Indexing LayerYour documents (PDFs, Word files, spreadsheets, reports) and databases are processed, cleaned, and indexed into a searchable vector store.Each piece of text is turned into an “embedding” — a mathematical representation that captures its meaning.
- Retriever EngineWhen you ask a question, the system retrieves the most relevant chunks of information from your indexed data.This ensures the model has the context needed to answer accurately.
- LLM Generation LayerThe large language model (like GPT-5 or Llama 3) takes your question plus the retrieved context and generates a natural-language answer — grounded in your company’s data.This output can be displayed in a chatbot, dashboard, or even integrated into existing systems like Oracle, SAP, or custom portals.
The Role of Knowledge Graphs
While RAG brings context to unstructured information, Knowledge Graphs bring structure and relationships to your enterprise data.
A Knowledge Graph represents your business entities (customers, suppliers, items, orders, contracts, organizations) and their relationships as a connected network of nodes and edges.
This makes it possible for AI systems to not only retrieve information, but to understand how that information relatesacross systems.
For example:
- A supplier node connects to purchase orders, invoices, and payments.
- An item node links to its lots, serials, subinventories, and quality status.
- A contract node relates to specific legal clauses, suppliers, and project cost centers.
When RAG is combined with a Knowledge Graph:
- The retrieval process becomes smarter — because the graph provides semantic relationships, not just text similarity.
- The answers become more explainable — as the AI can trace the reasoning path across entities.
- The system becomes more proactive — capable of detecting anomalies or suggesting insights based on how data is connected.
In other words, RAG retrieves what you need; the Knowledge Graph explains how it all fits together.
Real Business Applications
1. Financial and Compliance Teams
RAG + Knowledge Graphs can instantly answer questions about accounting rules, CNAB layouts, or tax legislation (SPED, EFD-Reinf, IBS/CBS, etc.) while mapping how each rule connects to suppliers, invoices, and GL accounts in your Oracle setup.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics
Teams can query inventory data conversationally — “Which lots expire in the next 60 days and belong to suppliers under contract type X?”
The Knowledge Graph connects WMS data to purchasing and quality, giving a 360° view.
3. Procurement and Contracts
A contract query not only retrieves the document text but also links it to the supplier, negotiation history, and payment schedules through the Knowledge Graph.
Perfect for audit and compliance automation.
4. Knowledge Management and Training
New employees can ask: “What are the receiving rules for items in the 001 org?”
The RAG layer retrieves the policy, while the Knowledge Graph shows which transactions, screens, and suppliers are affected.
Integration with Your Existing Systems
RAG and Knowledge Graphs can connect to:
- Oracle EBS R12, Oracle Cloud ERP, SAP, or Dynamics
- Databases (Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL)
- Document repositories (SharePoint, Google Drive, S3, internal portals)
- BI dashboards and logs (OAS, Power BI, Databricks, etc.)
This creates a unified knowledge fabric, without duplicating or moving data — ensuring security, traceability, and compliance.
In Oracle environments, for instance, your Knowledge Graph can represent relationships between tables like PO_HEADERS_ALL, PO_LINES_ALL, AP_INVOICES_ALL, and RCV_TRANSACTIONS, while RAG provides contextual narrative from procedures, specifications, or user manuals.
Business Value and ROI
Implementing RAG and Knowledge Graphs can generate measurable results:
- Reduce information retrieval time by up to 80%
- Improve decision quality through verified and interconnected knowledge
- Accelerate onboarding by providing guided, contextual explanations
- Enhance compliance with auditable relationships and traceable sources
- Enable predictive and proactive insights using connected business logic
Instead of building yet another silo, this architecture connects all silos intelligently.
Security and Governance
Both RAG and Knowledge Graphs respect your company’s data policies.
All access and queries are auditable, and documents or structured data remain in their original locations.
Only the relevant context or metadata is used during query processing, ensuring compliance with LGPD and internal governance standards.
The Future of Enterprise Knowledge
RAG and Knowledge Graphs represent the next phase of enterprise intelligence — context-aware and relationship-aware systems that understand your business holistically.
Soon, every organization will have a corporate knowledge layer — a secure AI system that can reason over its own data, explain relationships, and provide accurate, evidence-based answers.
The question is not if you’ll adopt these technologies, but how strategically you’ll design them for your business.
Final Thoughts
Building RAG and Knowledge Graph–based solutions is not just about deploying AI.
It’s about giving your organization a real-time, explainable, and trusted understanding of its operations.
Your company already owns the data and the documentation.
RAG retrieves it. The Knowledge Graph connects it. Together, they turn information into intelligence.